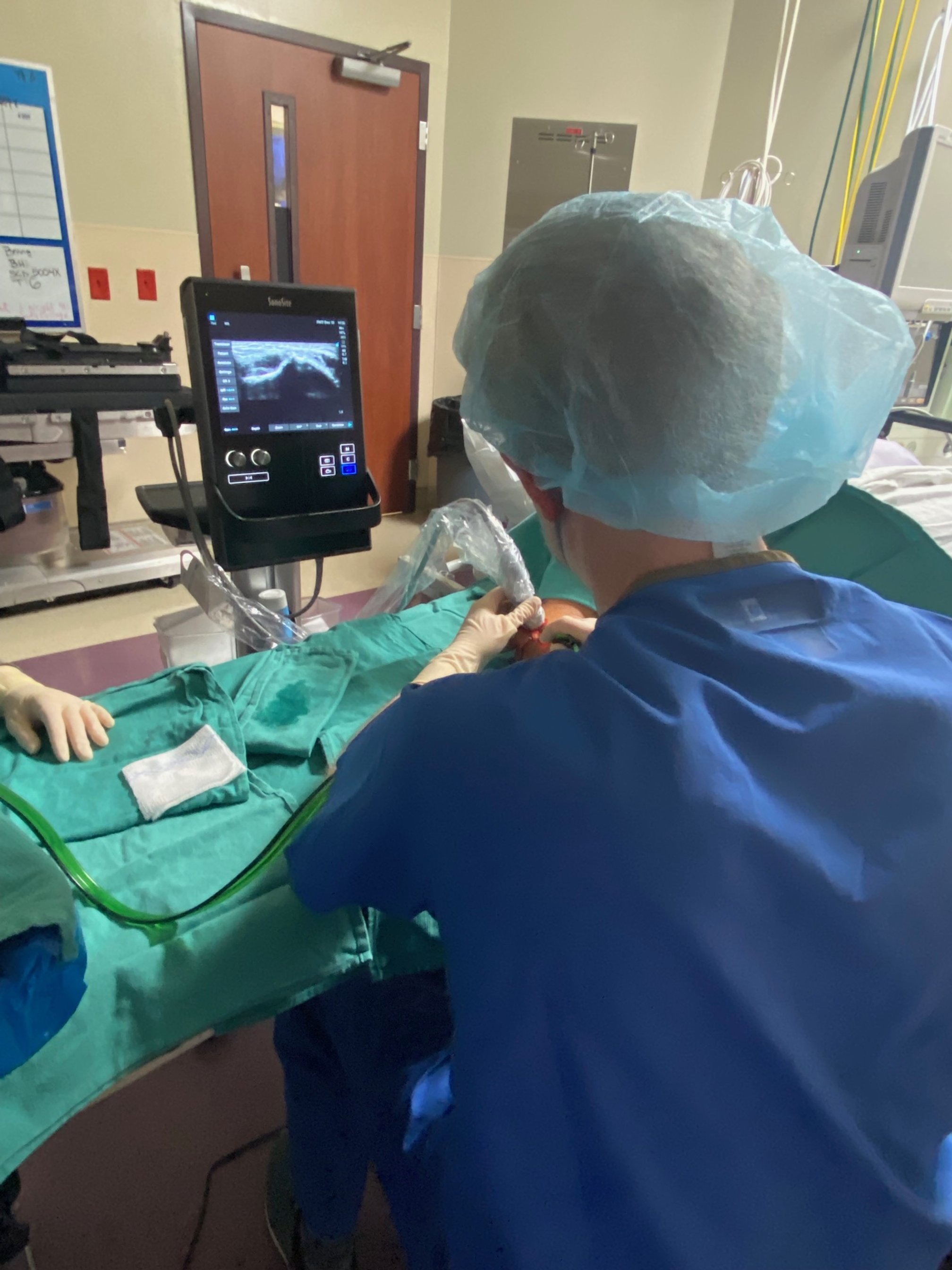
TENex for TENnis Elbow
/At times, tennis elbow, also known as lateral epicondylitis, can be so stubborn that an advanced procedure is needed to overcome this condition. There are two basic types of surgeries used to treat this condition. The first and by far our favorite is a percutaneous tenotomy under ultrasound guidance, commonly referred to as the Tenex procedure. The other is an open release of the tendon which involves cutting the tendon off the bone. Let’s briefly highlight the differences between the two:
Anesthesia
Tenex: Local-lidocaine injection only
Open: General- patient is put to sleep
Incision Size
Tenex: 1/4 inch
Open: 1-2 inches
Trauma To Tissue
Tenex: Minimal
Open: Moderate
Infection Risk
Tenex: Minimal
Open: Mild
Sutures/Stitches
Tenex: None
Open: 1-2 layers required
Recovery Time
Tenex: 2-6 months
Open: 4-12 months
Success Rate
Tenex: 90-95%
Open: 75-90%
Are we biased towards the Tenex? You better believe it! Look at those comparisons above. In our mind, it’s an obvious choice: the Tenex procedure is the better overall option. Why do more physicians not perform the Tenex procedure? Because you are required to have proficiency in musculoskeletal ultrasound to perform this procedure. Not many physicians have taken the time and made the investment in ultrasound-guided procedures, so they tend to revert to the more traditional, sometimes higher-risk and less successful options.
We’ve performed more Tenex procedures in Middle Tennessee than any other physician. So, if you, a loved one or friend has tennis elbow, then come see us!
F. Clarke Holmes, M.D.
Bet You Didn't Know: Tennis Elbow
/Tennis Elbow, one of the most common conditions seen by an orthopedist, is one our favorite diagnoses to make. Why?…because we are almost always able to see complete resolution of the symptoms. Plus, we have numerous traditional and innovative tools in the toolbox to help our patients overcome this often stubborn and humbling condition. Here are some fast facts about tennis elbow you probably did not know:
-90% of those with tennis elbow, also known as lateral epicondylitis, do not play tennis. Weight-lifting, frequent typing, CrossFit, repetitive labor in one’s work or with household chores are frequent causes.
-Teenagers almost never get tennis elbow. Why? They have an amazing ability for their tendons to recover much faster and more efficiently than middle age and older individuals.
-Lateral epicondylitis is the medical term for tennis elbow and may be one of the more misnamed conditions in orthopedics. This implies there is inflammation of the bone on the outside of the elbow, but instead, this is a tendon problem.
Patients who receive cortisone/steroid injections are often better in the short term but worse in the long term. Our own experience and the medical literature validates this.
Neovascularization, essentially new blood for vessel formation, commonly occurs in advanced cases of tennis elbow. Increased blood flow seems like it would be a good thing for the tendon, but in reality, is a sign of more advanced tendon damage.
We believe that adjacent to those new blood vessels in the tendon are new nerves that are very hypersensitive and only make you feel pain. This is why many patients with advanced cases of tennis elbow complain of “burning” over the lateral elbow.
Platelet-rich plasma injections, now a commonly used and innovative treatment option for many orthopedic conditions, were first studied in the medical literature about 15 years ago in treating tennis elbow. PRP remains one of our advanced treatment options for tennis elbow.
One of our best treatment options for very stubborn cases of tennis elbow is the Tenex procedure. Not many people know about Tenex because we are one of the few physicians in middle Tennessee who have expertise in performing this procedure. We’ve done it for 11 years, and it involves a tiny incision, local anesthesia only, and use of a small needle-like device to excise the unhealthy part of the tendon. No stitches are required and only about two minutes of actual treatment time in the operating room. It carries a 95% success rate in our experience.
If you have pain on the outside of your elbow that is interfering with your quality of life, then come see us. We will have some great options for you!
F. Clarke Holmes, M.D.
TENex Gets a 10!
/Are you looking for permanent relief from tennis or golfer’s elbow? Are you tired of having elbow and forearm pain with lifting, gripping and grabbing, even with items like your phone or coffee mug? Are your workouts in the gym or tennis or golf severely hampered by these symptoms? Well, then look no further than the Tenex procedure. This is an innovative minimally invasive procedure developed 13 years ago in conjunction with the renowned Mayo Clinic. Dr. Holmes has performed more Tenex procedures than any other physician in middle Tennessee over the past 10 years.
The Tenex procedure, also termed a percutaneous tenotomy, is a great option for tennis or golfer’s elbow (also known as lateral or medial epicondylitis, respectively) that has not healed with rest and other possible treatments such as medications, physical therapy, injections, or bracing.
We go to the operating room, give the patient an injection of lidocaine only, a numbing agent. We get to avoid the sedation, cost and side effects of general anesthesia (getting put to sleep).
A tiny incision of about 1/4 inch is made. A small hand piece with a needle tip is inserted through the incision. Under ultrasound-guidance, this tip is inserted to the damaged part of the tendon and ultrasonic energy allows the tip to debride and remove the unhealthy portion of the tendon while leaving the healthy portion alone. Two minutes of treatment time or less and you are on the road to recovery.
No stitches required, just a few small steri-strips, followed by a small dressing and you are out the door, headed towards tendon healing, and eventually becoming pain-free.
Post-operatively, you wear a wrist splint for at least 2 weeks, and we restrict lifting for about 6 weeks. Our golfers, tennis players and weightlifters can usually gradually resume these activities at the 3-month mark. There is no “quick fix” for these conditions, yet Tenex offers a permanent solution to an often-stubborn problem.
We’ve done in the range of 500 of these procedures over the past 11 years with excellent results.
This procedure really beats the option of steroid injections, which often make the condition worse in the long term. The alternative to Tenex is a larger surgery requiring a 2-inch incision and a much longer recovery.
In our book, the Tenex procedure gets a rating of 10!
Will My Heel Pain Ever Go Away?
/In middle-age individuals, 90% of the time, heel pain is caused by plantar fasciitis. The plantar fascia is a soft-tissue band, technically a ligament, that supports the hindfoot and midfoot. It is quite prone to inflammation, degeneration and tearing. It is a stubborn problem to both endure and to treat, and commonly becomes a condition that last months to occasionally years. However, do not fear, we have solutions for you!
How Does it Present?
· Heel pain, often sharp, with the first few steps out of bed and after a long day on your feet
· Pain when rising from a seated position after prolonged sitting, such as in a car
· In endurance athletes, pain during and after exercise
· Tenderness on the bottom of the foot, specifically at the heel where the plantar fascia originates
Why Did I Get This?
· Age- middle-agers are prone to this, as they are very active, but their rate of tissue breakdown exceeds their body’s repair rate. This is why younger individuals do not typically get this problem. They have a faster healing rate.
· Poor footwear- shoes that are flimsy, too old or generally unsupportive contribute
· Weight- gaining weight or being overweight overloads the tissue at the lowest point of our body
· Too much activity/overuse- runners, walkers, and athletes repetitively load the plantar fascia, and at times, are in a situation of overuse or too much, too soon
· Poor biomechanics- tight or weak calf muscles, a high arch or flat foot or a foot that excessively pronates or supinates can all contribute
How Do I Treat It?
Patience is the key. Let’s repeat that….patience is the key. This condition often requires months of treatment. Recovery can be slow. The underlying risk factors listed above must be corrected. What works for one patient may not be the best treatment for another. Care must be individualized.
· Rest- yes, this is a dirty, four-letter word for many patients. Plantar fasciitis will NOT improve as long as one continues to run, walk or exercise to the same degree. Sometimes, activity modification will work- fewer miles, less frequent high-impact exercise and/or trying something lower impact such as biking or swimming
· Improve the footwear and minimize going barefoot- remember with shoes, you often get what you pay for. Don’t go cheap!
· Physical Therapy- helps most patients, can be curative for those with mild cases. Will not get the job done by itself for moderate to severe cases.
· Orthotics/Inserts- over-the-counter or custom. OTC ones are less expensive and worth a try for mild cases. Custom are more expensive but are more successful for most patients. Orthotics alone usually will not cure plantar fasciitis. Other treatments must be combined.
· Anti-inflammatory medications- helpful in mild cases caught early. Not helpful in more severe cases or in patients that have had the problem for months or longer.
· Cortisone injections- occasionally helpful, more often harmful. We rarely utilize these, as they don’t promote healing, only reduce inflammation and can increase the risk of further tearing of the fascia. NEVER get a series of 3 cortisone injections as recommended by some.
· Orthobiologic injections- very helpful for most. These are meant to “heal the heel!” Platelet-rich plasma injections introduce numerous growth factors to the area to improve the tissue environment and thus, are typically successful in promoting healing of the fascia while reducing pain and improving function. These are game-changing injections and ones we have provided under ultrasound-guidance successfully now for many years.
· Surgery- we favor a minimally-invasive procedure called the Tenex procedure. Tiny incision, local anesthesia only, no stitches required with minimal healthy tissue disruption. The “old-school” surgeries require larger incisions and involve “releasing”/cutting the fascia off the bone, are less successful, higher risk and have been abandoned by many orthopedic surgeons.
What to Avoid:
1) Stretching the bottom of the foot. An example is when you pull the toes back towards you. Most cases of PF involve inflammation and/or tearing of the fascia. Stretching damaged or inflamed tissue is often counterproductive
2) Pushing through the pain with exercise. If you have PF, you have to relatively rest, which may mean temporarily discontinuing running, walking, jumping, etc. or at least, reducing your distance or frequency of these activities.
3) Skimping on shoes and/or orthotics. The old adage, “you get what you pay for…” applies here. Think of purchasing high-quality athletic and everyday shoes as well as orthotics (inserts) as an investment in your health and quality of life. At times, the more expensive orthotics are worth the extra cost.
In conclusion, heel pain affects a high percentage of middle-age individuals and can range from a nuisance problem to a disabling one. The key here is to seek care early and from someone who can customize a well-constructed treatment plan for you that has a variety of quality interventions. We are here to help!
My Elbow Really Hurts, and I Feel Like a Wimp!
/We hear this comment or one very similar to it on a frequent basis. Good ole’ tennis elbow, also know as lateral epicondylitis. Despite these names, this is not a problem limited to tennis players and does not typically involve the bone on the outside of the elbow named the lateral epicondyle. It is actually a tendon problem. The common extensor tendon on the outside of the elbow is highly involved in gripping, grabbing and lifting. When you shake someone’s hand, this tendon is under a lot of stress. When you lift the coffee mug with a handle, the positioning of your wrist transmits stress to this tendon. When you pull your sheets up to you when in bed, the position and action of the wrist and forearm send stress to this tendon. Finally, when this tendon is inflamed and/or partially torn, it HURTS! I mean, it really hurts. You are not a wimp for complaining about tennis elbow. Fortunately, this is one of my favorite conditions to treat. Why? For many reasons: we usually can cure this problem. Patients are so grateful to see this pain go away. Finally, it’s gratifying to see patients return to things they love to do after successful treatment such as tennis, golf, weight lifting, gardening and even typing!
Turning our attention to treatment options, there are traditional and innovative options. At Impact Sports Medicine and Orthopedics, we specialize in both types:
Traditional:
1) REST and changing the biomechanics- how and how much you lift, grip and grab
2) A wrist splint- yes, immobilizing the wrist and forearm unload the tendon far more than immobilizing the elbow
3) A cortisone injection- in our hands, 90% of patients experience relief with an ultrasound-guided injection. However, since tendon damage is often the cause of the stubborn pain, cortisone, at times, may only provide temporary benefit.
4) Physical Therapy- helpful in changing the biomechanical problems that led to the tendon damage. However, the benefit can be limited if tendon is partially torn.
Innovative:
1) The Tenex procedure- a true game-changing minimally-invasive procedure. This is our favorite option for those patients that have not improved with the traditional treatments. Local anesthesia only, a tiny incision, 2 minutes of tendon treatment with a small probe, no stitches, typically covered by insurance and a 90% success rate. How does that sound? We've loved this procedure for 7+ years.
2) Orthobiologic Injections- platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections are very solid choices, isolating and concentrating the platelets from you own blood. This becomes a solution rich in human growth factors utilized to stimulate healing of the tendon.
3) Nitroglycerin patches- placed on the skin over the tendon, these are good choices for those patients needing something extra, but prefer a treatment that is non-invasive. These work by producing nitric oxide in the tissues, which then can be responsible for tendon healing.
In summary, we hate that you have "tennis elbow," but always appreciate the opportunity to treat you. It's our mission to make this common cause of elbow pain leave your life and never return! Let us know if we can help.
-F. Clarke Holmes, M.D.
Tennis Elbow: The Most Misnamed Orthopedic Condition
/Fewer than 10% of patients that have tennis elbow actually play tennis. In addition, the medical term for this condition is "lateral epicondylitis." This also is misnamed. Why? The lateral epicondyle is the bony prominence on the outside of the elbow. This sometimes stubborn condition is not a bone problem, but a tendon problem, actually involving what we call the common extensor tendon. This also can be a very humbling condition. It can cause significant pain with some simple, everyday activities- lifting a coffee cup, shaking hands, pulling your bedsheets, just to name a few. Why you ask? Stress to this tendon is not only related to the weight of a lifted object, but also the arm and wrist position. Certain positions cause overloading of the damaged and/or inflamed tendon. Turning our attention to treatment options, there are traditional and innovative options. At Impact Sports Medicine, we actually specialize in both types:
Traditional:
1) REST and changing the biomechanics- how and how much you lift, grip and grab
2) A wrist splint- yes, immobilizing the wrist and forearm unload the tendon far more than immobilizing the elbow
3) A cortisone injection- in our hands, 90% of patients experience relief with an ultrasound-guided injection. However, since tendon damage is often the cause of the stubborn pain, cortisone, at times, may only provide temporary benefit.
4) Physical Therapy- helpful in changing the biomechanical problems that led to the tendon damage. However, the benefit can be limited if tendon is partially torn.
Innovative:
1) The Tenex procedure- a true game-changing minimally-invasive procedure. This is our favorite option for those patients that have not improved with the traditional treatments. Local anesthesia only, a tiny incision, 2 minutes of tendon treatment with a small probe, no stitches, covered by insurance and a 90% success rate. How does that sound? We've loved this procedure for 6+ years.
2) Orthobiologic injections- platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections are very solid choices, isolating and concentrating the platelets from you own blood. This becomes a solution rich in human growth factors utilized to stimulate healing of the tendon
3) Nitroglycerin patches- placed on the skin over the tendon, these are good choices for those patients needing something extra, but prefer a treatment that is non-invasive. These work by producing nitric oxide in the tissues, which then can be responsible for tendon healing.
In summary, we hate that you have "tennis elbow," but love the opportunity to treat you. It's our mission to make this common cause of elbow pain leave your life and never return! Let us know if we can help.
My Heel is Killing Me! What is This and How Do I Get Rid of It?
/In middle-age individuals, 90% of the time, heel pain is caused by plantar fasciitis. The plantar fascia is a soft-tissue band, technically a ligament, that supports the hindfoot and midfoot. It is quite prone to inflammation, degeneration and tearing. Let’s quickly dive into this common cause of heel pain.
How Does it Present?
· Heel pain, often sharp, with the first few steps out of bed and after a long day on your feet
· Pain when rising from a seated position after prolonged sitting, such as in a car
· In endurance athletes, pain during and after exercise
· Tenderness on the bottom of the foot, specifically at the heel where the plantar fascia originates
Why Did I Get This?
· Age- middle-agers are prone to this, as they are very active, but their rate of tissue breakdown exceeds their body’s repair rate. This is why younger individuals do not typically get this problem. They have a faster healing rate.
· Poor footwear- shoes that are flimsy, too old or generally unsupportive contribute
· Weight- gaining weight or being overweight overloads the tissue at the lowest point of our body
· Too much activity/overuse- runners, walkers, and athletes repetitively load the plantar fascia, and at times, are in a situation of overuse or too much, too soon
· Poor biomechanics- tight or weak calf muscles, a high arch or flat foot or a foot that excessively pronates or supinates can all contribute
How Do I Treat It?
Patience is the key. This condition may require a month or a year of treatment. Recovery can be slow. The underlying risk factors listed above must be corrected. What works for one patient may not be the best treatment for another. Care must be individualized.
· Rest- yes, this is a dirty, four-letter word for many patients. Plantar fasciitis will NOT improve as long as one continues to run, walk or exercise to the same degree. Sometimes, activity modification will work- fewer miles, less frequent high-impact exercise and/or trying something lower impact such as biking or swimming
· Improve the footwear and minimize going barefoot- remember with shoes, you often get what you pay for. Don’t go cheap!
· Physical Therapy- helps most patients, can be curative for those with mild cases. Will not get the job done by itself for moderate to severe cases
· Orthotics/Inserts- over-the-counter or custom. OTC ones are less expensive and worth a try for mild cases. Custom are more expensive but more beneficial for most patients. Orthotics alone will not cure plantar fasciitis. Other treatments must be combined
· Anti-inflammatory medications- helpful in mild cases caught early. Not helpful in more severe cases or in patients that have had the problem for months or longer
· Cortisone injections- occasionally helpful, occasionally harmful. We rarely utilize these, as they don’t promote healing, only reduce inflammation and can increase the risk of further tearing of the fascia. NEVER get a series of 3 cortisone injections as recommended by some.
· Orthobiologic injections- very helpful for most. These are meant to “heal the heel!” Platelet-rich plasma injections introduce numerous growth factors to the area to promote tissue regeneration. These are game-changing injections and ones we have provided under ultrasound-guidance successfully now for many years.
· Surgery- we favor a minimally-invasive procedure called the Tenex procedure. Tiny incision, local anesthesia only, no stitches required with minimal healthy tissue disruption. The “old-school” surgeries require larger incisions and involve “releasing”/cutting the fascia off the bone, are less successful, higher risk and have been abandoned by most orthopedic surgeons
In conclusion, heel pain affects a high percentage of middle-age Americans and can range from a nuisance problem to a disabling one. The key here is to seek care early and from someone who can customize a well-constructed treatment plan for you that has a variety of quality interventions. We are here to help!