Orthopedic Injections: What Not To Do
/Injections are one of the most commonly used interventions in an orthopedic practice. Yet, where, how and what is injected is of vital importance, and certain approaches are just not in the best interest of the patient. Here are injections we prefer you avoid:
1) Injections for musculoskeletal conditions given in a chiropractic or primary care office. Both chiropractors, chiropractic mid-levels (NPs and PAs) along with PCPs all often do a great job in their respective specialties. However, giving injections optimally is just not in their wheelhouse. Therefore, if an injection is needed or suggested, then seek the expertise of an orthopedic specialist.
2) Receive a series of steroid injections for soft tissue conditions, such as plantar fasciitis, tennis/golfer’s elbow or gluteal tendinopathy (often mislabeled as “hip bursitis”). We often use the statement, “better in the short term, worse in the long-term.” This really applies to situations when multiple steroid injections are given in a short period of time, as they ultimately can lead to further breakdown and tearing of these tendons/fascia.
3) Receive a steroid injection for Achilles, patellar or quadriceps tendon problems. These tendons are much higher risk for rupture, especially if exposed to a steroid injection. If anyone suggests a steroid for one of these conditions, then RUN (figuratively)!
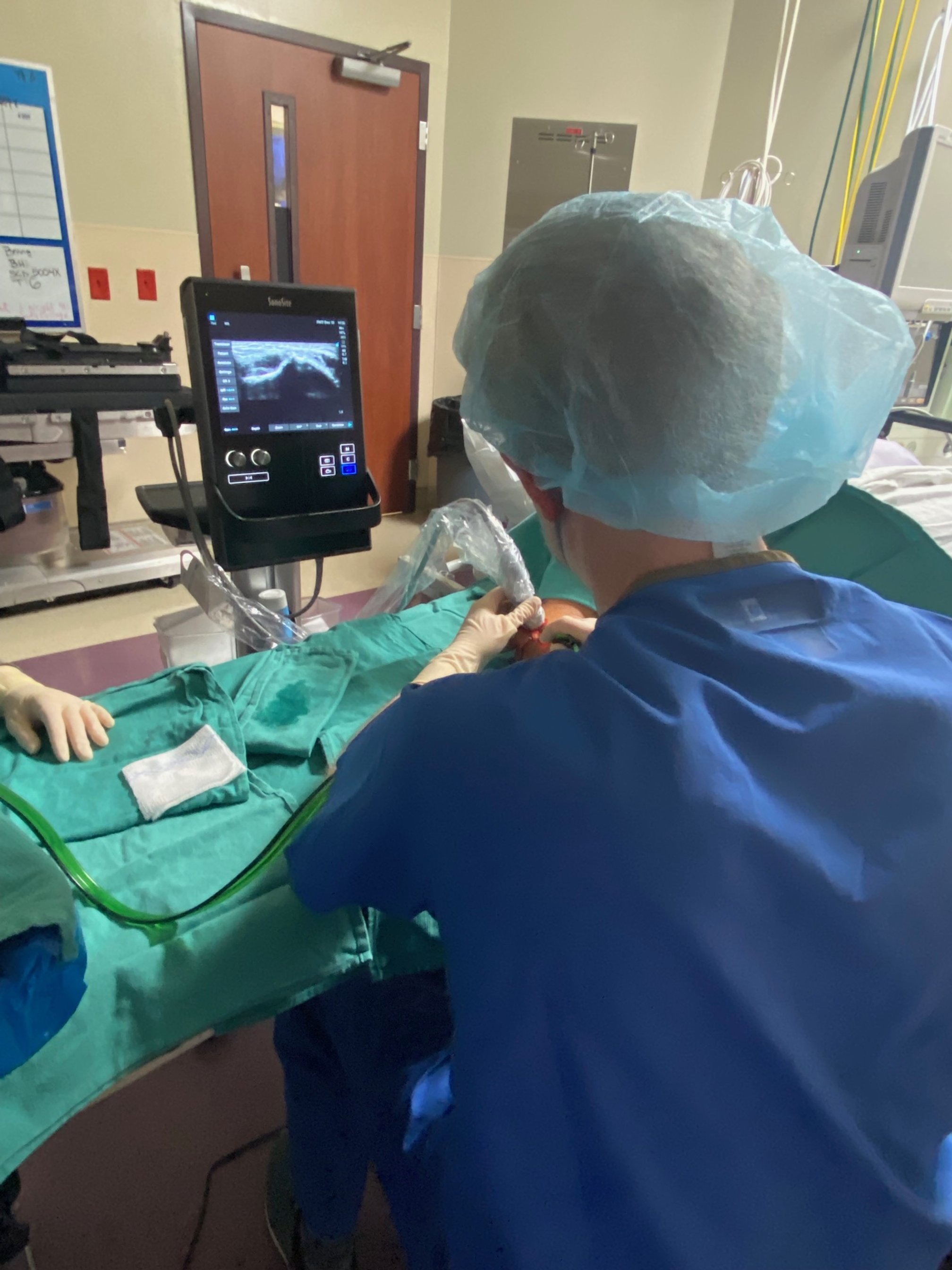
4) Pay top dollar for an orthobiologic injection such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP) without ultrasound guidance. It’s your choice to have this injection if it’s non-guided but just realize that accuracy is so important with this type of injection. There is no way to ensure the solution is making it to the intended area without ultrasound.
5) Receive “stem cell” injections that do not come from your own tissue. If a stem cell injection is being suggested, it should be derived from your bone marrow or your adipose (fat) tissue. Most of these products "ordered for you” do not actually contain any live stem cells, and at this point, are not approved by the FDA for usage in musculoskeletal conditions.
As always, let us know if we can help you!
F. Clarke Holmes, M.D.
Three Roadblocks to Your Health: Time, Fear and Money
/
Time: we’re all so busy, at least we think we are. Let’s be real, going to see the doctor does take time. Driving, parking, filling out forms, waiting, talking, testing and deciding. The average visit from start to finish. meaning door-to-door is in the range of 2 to 3 hours. Yet, that 2 to 3 hours could be the difference in you getting a diagnosis, relieving anxiety, feeling better, promoting better function and doing something that can help your body long-term. Are you willing to binge watch a show for 2 to 3 hours? Are you willing to go to dinner for 2 to 3 hours? Are you willing to surf social media and watch videos for 2 to 3 hours? Are you willing to go to the mall for 2 to 3 hours? Are you willing to go to the gym for 2 to 3 hours? If the answer to these questions is “yes,” then you definitely have time for a doctor’s visit.
Fear: so many patients skip that doctor’s visit because of fear of a frightening diagnosis, a recommendation that surgery is necessary or because of potential expenses that come with that visit and subsequent treatment. Here’s the good news: often that fear fades away once you get into the doctor’s office and actually are able to learn why you have certain symptoms and then are able to develop a plan of action. I’ve seen it for decades, as many patients, even when given news that they did not want to hear, find a sense of relief. Frequently though, we are able to provide good news and reassurance, calming the patient’s fears. In a nutshell, fear of the unknown is often much greater than the fear of the known. More good news here… 95% of patients that present to our office do not require surgery!
Money: sometimes the most expensive course of medical treatment is the one that was developed late in the game. Meaning, if a patient would have sought treatment earlier, a much less expensive plan of action could have been developed. There is no greater investment than the one in your health. We are all willing to spend money on trips, hobbies, clothes, restaurants, cars, etc. While all these can have value, they don’t hold a candle when compared to your health. So, make sure that you are budgeting enough money to pay for your necessary healthcare. Finally, when making financial decisions about your health, attempt to think long-term, not just short-term.
As always, let us know if we can be of assistance to you!
F. Clarke Holmes, M.D.
Here Comes Volleyball Season: We Are Ready in the Orthoworld!
/Volleyball season is fast-approaching. Today, let’s discuss the four most common areas of injury, treatment and prevention.
Volleyball was my sport as a youth. I played all year-round, and if I wasn’t in practice or a tournament, I was working out. But is the constant wear and tear on our bodies without rest hurting us even at a young age? In parts, yes. We commonly see athletes whose injuries could have been prevented with a short period of rest or prevention methods. Let’s talk about that:
1. Ankle
Most common: ankle sprain. It comes as no surprise that ankle injuries are one of the most common injuries seen in volleyball. Initial treatment includes RICE (rest, ice, compression, and elevation). However, it is always wise to see an orthopedic provider who can help guide you in treatment, prevention, and return to play. What many people do not know is younger children and teenagers’ growth plates are still open and are also at risk of injury with a twist of the ankle. When growth plates are still open, they are the most vulnerable and at risk for a Salter-Harris fracture which involves the growth plate. After growth plates close, the ligaments become the most vulnerable. I like to tell my patients that ligaments are like the candy Laffy Taffy. Once they are stretched out, they don’t necessarily return to their original state. Thus, prevention and strengthening are imperative.
Prevention: ankle range of motion, strengthening, and balance exercises; keeping footwear up to date; purchasing well-fitting and high-quality footwear; and ankle braces during practice and games.
2. Knee
Most common: patellar tendonitis (chronic) and ACL tears (acute)
Patellar tendonitis, also known as jumper’s knee, is very common due to the amount of jumping volleyball requires. Many times, the athlete will localize the pain right under the kneecap at the proximal aspect of the patellar tendon. Our office utilizes diagnostic ultrasound to look at the characteristics of patellar tendon, identify if there is tearing, compare it to the unaffected size, and determine if there is any new blood vessel formation (neovascularization). Prevention and treatment include stretching and strengthening exercises, a period of rest from jumping, and a patellar tendon strap. Short-term anti-inflammatories can helpful. In difficult cases, we can turn to platelet-rich plasma injections (PRP). Those with an open growth plate at the tibial tuberosity are at risk of developing Osgood-Schlatter’s.
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) tears: Volleyball is relatively high risk for ACL tears due to potentially landing awkwardly after a jump or during pivoting maneuvers frequently required. The ACL is under the most load when the knee is under sudden valgus (knock-kneed) stress. The best preventative options are to strengthen the outer hip, upper thigh, and gluteal muscles along with jump-training techniques to help protect the knee. If diagnosed with an ACL tear, treatment can be conservative or surgical. Those who wish to continue participating in high-risk sports generally opt for surgical intervention.
3. Shoulder
Most Common: Impingement, Labral Tears, Instability, and Rotator Cuff Tendinitis
Those who are hitters in volleyball are at risk for all of these shoulder conditions. Once again, relative rest, recovery, and strengthening are imperative in preventing these conditions. Improvement in form and hitting techniques are often helpful. Injections (occasional steroid, but more commonly PRP) can play a role in more difficult cases.
4. Low Back
Most Common: Lower Back Strain/Sprain (acute) or Spondylolysis
Volleyball requires repetitive bending, twisting, and hyperextension movements which put the low back in vulnerable positions. The biggest takeaway is if you or your child is experiencing low back pain that is not relieved after a couple weeks, please see an orthopedic provider. This could indicate a spondylolysis (a stress fracture) or stress reaction in the bones of the lumbar spine. Low back strains/sprain can be muscular or ligamentous and tend to improve within 2 weeks. If that’s not the case, then we often look for spondylolysis or even disc problems.
As mentioned, strengthening and adequate rest while allowing our bodies to recover are the best ways to prevent these common injuries. However, if these injuries occur and you or your child’s symptoms are unresolved beyond a week or two, please give us a call!
Taylor Moore, NP
Bet You Didn't Know: Tennis Elbow
/Tennis Elbow, one of the most common conditions seen by an orthopedist, is one our favorite diagnoses to make. Why?…because we are almost always able to see complete resolution of the symptoms. Plus, we have numerous traditional and innovative tools in the toolbox to help our patients overcome this often stubborn and humbling condition. Here are some fast facts about tennis elbow you probably did not know:
-90% of those with tennis elbow, also known as lateral epicondylitis, do not play tennis. Weight-lifting, frequent typing, CrossFit, repetitive labor in one’s work or with household chores are frequent causes.
-Teenagers almost never get tennis elbow. Why? They have an amazing ability for their tendons to recover much faster and more efficiently than middle age and older individuals.
-Lateral epicondylitis is the medical term for tennis elbow and may be one of the more misnamed conditions in orthopedics. This implies there is inflammation of the bone on the outside of the elbow, but instead, this is a tendon problem.
Patients who receive cortisone/steroid injections are often better in the short term but worse in the long term. Our own experience and the medical literature validates this.
Neovascularization, essentially new blood for vessel formation, commonly occurs in advanced cases of tennis elbow. Increased blood flow seems like it would be a good thing for the tendon, but in reality, is a sign of more advanced tendon damage.
We believe that adjacent to those new blood vessels in the tendon are new nerves that are very hypersensitive and only make you feel pain. This is why many patients with advanced cases of tennis elbow complain of “burning” over the lateral elbow.
Platelet-rich plasma injections, now a commonly used and innovative treatment option for many orthopedic conditions, were first studied in the medical literature about 15 years ago in treating tennis elbow. PRP remains one of our advanced treatment options for tennis elbow.
One of our best treatment options for very stubborn cases of tennis elbow is the Tenex procedure. Not many people know about Tenex because we are one of the few physicians in middle Tennessee who have expertise in performing this procedure. We’ve done it for 11 years, and it involves a tiny incision, local anesthesia only, and use of a small needle-like device to excise the unhealthy part of the tendon. No stitches are required and only about two minutes of actual treatment time in the operating room. It carries a 95% success rate in our experience.
If you have pain on the outside of your elbow that is interfering with your quality of life, then come see us. We will have some great options for you!
F. Clarke Holmes, M.D.
Three Common Financial Misconceptions in the Medical World
/Understanding the complexity of various medical expenses can be overwhelming for a patient. We medical professionals are patients too! Even for us, sometimes the numbers just don’t make sense. At Impact Sports Medicine and Orthopedics, our desire is to educate patients regarding the value of these office visits and procedures and their potential out-of-pocket costs, so that they can make informed decisions regarding their health care from both a medical and economic perspective.
Here are three common misconceptions when it comes to medical expenses:
If my physician is not in-network with my insurance company, my medical expenses will be higher: until patients meet their deductibles, they typically will pay out-of-pocket for office visits, diagnostic tests and procedures. The amount a patient pays can also depend on a patient’s out-of-network provisions in their plan and/or the amount an out-of-network provider chooses to bill the patient. Often an out-of-network provider will ask the patient to pay cash, and this amount can be and often is less than the contracted amount an in-network provider has with your insurance. Example: you have Insurance X, a plan that has accepted very few in-network physicians. You have not met your deductible and you see an in-network orthopedic specialist for a consult. You have an office visit and x-rays. Insurance X allows $150 for the office visit and $50 for the x-rays. You now owe that in-network physician $200. Alternatively, you see a provider at our practice as we are in-network with most insurance plans, but not with Insurance X. We charge you $120 for the office visit and $30 for x-rays. Thus, your bill with us is $150, a $50 savings compared to the in-network provider.
If a procedure is not covered by insurance, it will cost me more in the long run: as an example, let’s use a procedure such as a platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injection. PRP has been used in orthopedics for 15 years. It has never been covered by insurance (although it should be in certain circumstances…that’s a whole different conversation). You have stubborn plantar fasciitis. You’ve done all the typical treatments, but your heel still really hurts. You consult with a foot surgeon who offers an open or endoscopic plantar fascia release surgery. Guess what, your insurance covers this procedure! However, you have a $5000 deductible, and you are nowhere near meeting this. This surgery will have charges from the surgery center, the anesthesiologist and the foot surgeon. Let’s say that your total cost for this surgery is $3000 with a 75% success rate, a 4-month recovery and some risk of additional complications. Compare this to one or two PRP injections, with each injection costing you $800. PRP, in our opinion, will have similar success rates and recovery times with fewer complications. $1600 for PRP versus $3000 for the surgery, even though the surgery is “covered by insurance.”
When it comes to an office visit or the same procedure done at different practices, insurance companies pay or allow the same amount for each physician/practice: did you know that all practices, hospitals and other medical businesses have contracted rates of payments with private insurers (non-Medicare, non-Medicaid)? If a physician is part of a bigger organization such as a hospital or a large private practice, then that group typically has greater negotiating power and can obtain higher reimbursement rates from the insurance companies. These rates have nothing to do with the quality of medical care, the training or experience level of the providers or the success rates of their interventions. So, let’s say you see a physician associated with a hospital system. You haven’t met the deductible, and you are billed for a Level 4 new patient visit. Your insurance allows $200 for that visit to that provider. Alternately, your household family member sees a physician at a smaller practice like ours, also is billed for a Level 4 new patient visit, yet the same insurance only allows for $150 for that visit, even though the same level of care was provided. So, you owe $50 more to that hospital-based practice than your family member owes to the smaller private practice. Thus, it’s important to realize that often cost really does vary based on who you are seeing, and your cost is not associated with the quality of the care.
At Impact Sports Medicine, cost education and financial transparency are very important to the physician-patient relationship. We strive to provide the highest quality of care for a reasonable out-of-pocket cost to you.
F. Clarke Holmes, M.D.
TENex Gets a 10!
/Are you looking for permanent relief from tennis or golfer’s elbow? Are you tired of having elbow and forearm pain with lifting, gripping and grabbing, even with items like your phone or coffee mug? Are your workouts in the gym or tennis or golf severely hampered by these symptoms? Well, then look no further than the Tenex procedure. This is an innovative minimally invasive procedure developed 13 years ago in conjunction with the renowned Mayo Clinic. Dr. Holmes has performed more Tenex procedures than any other physician in middle Tennessee over the past 10 years.
The Tenex procedure, also termed a percutaneous tenotomy, is a great option for tennis or golfer’s elbow (also known as lateral or medial epicondylitis, respectively) that has not healed with rest and other possible treatments such as medications, physical therapy, injections, or bracing.
We go to the operating room, give the patient an injection of lidocaine only, a numbing agent. We get to avoid the sedation, cost and side effects of general anesthesia (getting put to sleep).
A tiny incision of about 1/4 inch is made. A small hand piece with a needle tip is inserted through the incision. Under ultrasound-guidance, this tip is inserted to the damaged part of the tendon and ultrasonic energy allows the tip to debride and remove the unhealthy portion of the tendon while leaving the healthy portion alone. Two minutes of treatment time or less and you are on the road to recovery.
No stitches required, just a few small steri-strips, followed by a small dressing and you are out the door, headed towards tendon healing, and eventually becoming pain-free.
Post-operatively, you wear a wrist splint for at least 2 weeks, and we restrict lifting for about 6 weeks. Our golfers, tennis players and weightlifters can usually gradually resume these activities at the 3-month mark. There is no “quick fix” for these conditions, yet Tenex offers a permanent solution to an often-stubborn problem.
We’ve done in the range of 500 of these procedures over the past 11 years with excellent results.
This procedure really beats the option of steroid injections, which often make the condition worse in the long term. The alternative to Tenex is a larger surgery requiring a 2-inch incision and a much longer recovery.
In our book, the Tenex procedure gets a rating of 10!
What Does "Being Proactive Over Reactive" Mean?
/Proactive Interventional Orthopedics (PIO)…a concept we will continue to promote. What does it mean in orthopedics to be proactive over reactive? Here are some examples and brief explanations:
Choose maintenance and more long-term injections over short-term steroid/cortisone injections: platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and hyaluronic acid injections often produce a more clinically significant and longer duration of benefit than steroid injections. For your knee and hip arthritis, tennis and golfer’s elbow and plantar fasciitis, just to name a few, choose these injections.
A course of physical therapy over exercises you simply found online: patient outcomes are generally better when you work with a physical therapist over Dr. Google or YouTube. We have fantastic relationships with physical therapists across Middle Tennessee and can work with you to find the best fit.
Regular use of supplements over prescription or over-the-counter medications: there’s a time and place for prescription meds when managing orthopedic conditions. However, for long-term management, we prefer options like curcumin/turmeric, collagen, and glucosamine/chondroitin. That being said, it’s always wise to consult with a physician before starting new supplements.
Don’t wait for your pain or disability to reach high levels before you seek treatment: orthopedic conditions treated early after the onset of symptoms and when pain and dysfunction are at a low level typically respond better to less-invasive treatments, and this early treatment can lower the risk of further damage to the joint or tissue.
Choose a specialist over a primary care physician for your orthopedics needs: PCPs work really hard and a do a great job to care for your overall health, but they do not necessarily have the expertise, the tools such as on-site imaging and advanced equipment or the time to dedicate to your orthopedic conditions.
Healthy eating patterns over a fad diet: weight loss is a vital part of the treatment plan when it comes to weight-bearing joint problems like hip and knee osteoarthritis. Through a variety of options, we can help you a structure a plan to gradually lose weight in a manner that the weight will stay off and through means that can be maintained for the long-term.
As always, let us know if we can help you overcome an injury, treat an orthopedic condition or find the pathway to greater wellness with an improved quality of life!
F. Clarke Holmes, M.D.
Frozen Shoulder: More Than Just a Winter Occurrence
/We’ve talked a lot about PIO (Proactive Interventional Orthopedics) recently and this concept really applies when it comes to a frozen shoulder, also known as adhesive capsulitis. This is a condition most commonly seen in middle-aged women around the time of menopause with the average age of a frozen shoulder being 51.
It starts as shoulder pain, often unrelated to a particular injury or overuse situation, and is followed by a very stiff shoulder with loss of motion. Although a frozen shoulder can be a self-limiting condition, with our interventions, we can greatly expedite the recovery process while alleviating pain.
Other risk factors for adhesive capsulitis include thyroid disease, diabetes and recent shoulder surgery. In the early “pain” stage, it’s often difficult to determine whether a patient has a frozen shoulder, osteoarthritis, or rotator cuff and/or biceps tendon problem. An MRI can be helpful, especially to see tendon or joint pathology, but in the presence of isolated adhesive capsulitis, the MRI can be normal or near normal. The next stage is the “stiff” or “frozen” stage, highlighted by the loss of motion both actively (what the patient can do) and passively (how someone else can move the shoulder). The final stage is the “thawing” or “recovery” stage. Each stage typically last 2-6 months, and early treatment often shortens these stages.
Being proactive and interventional often means an ultrasound-guided steroid injection into the joint. Without ultrasound guidance, it is often very difficult to achieve accuracy. This tends to be a very inflammatory condition, and thus, the potent anti-inflammatory effects of the steroid can provide rapid relief of pain. Early treatment within the first few weeks or months of the onset of the shoulder pain is the optimal path to a faster and more complete recovery. After that steroid injection, a rehab program, often made much more effective by the steroid injection, is the mainstay of treatment. 20% of patients with a frozen shoulder develop the same condition on the opposite shoulder within 5 years, so if pain in the other shoulder develops, it’s wise to seek treatment early.
Check out this brief article:
Steroid injection may be the best medicine for frozen shoulder - Harvard Health
If you think you may have a frozen shoulder, let us use PIO to help you!
F. Clarke Holmes, M.D.
Introducing the Concept of PIO
/As sports medicine providers, we are all about “getting ahead in the game.” Therefore, we have coined the term and are developing the concept of PIO (“pie-o”). PIO stands for proactive interventional orthopedics. You’ve possibly heard of interventional cardiologists or interventional radiologists. These are the physicians that are specialists in their field, but use less-invasive means to treat your condition. For example, the interventional cardiologist will perform angioplasty or a stent procedure, whereas the cardiovascular surgeon would be the physician to do the more-invasive coronary artery bypass surgery, when necessary.
In our field, PIO involves using less-invasive interventions such as injections, weight loss, physical therapy/exercise programs, and various supplements to “get ahead” of your musculoskeletal conditions that either currently are or will soon bring you pain, disability, and dysfunction. The field of orthopedics has typically been “reactive,” meaning you only go to the doctor when you have a significant problem. Unfortunately, when you are only reactive instead of proactive, treatment interventions become more invasive, higher risk, and sometimes less successful.
Here’s how we can use PIO to help you if have arthritis, tennis/golfer’s elbow, rotator cuff or Achilles problems, plantar fasciitis or other chronic conditions: we will customize a plan to reduce pain, improve function and quality of life in a cost-effective manner.
Here are links to two of our other blogs that explain the process and benefits of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections, often part of PIO treatment program.
Why Insurance Does Not Pay For Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections, But Why That Should Not Deter You — Impact Sports Medicine & Orthopedics (impactsportsnashville.com)
Five Simple Reasons You Should Consider Platelet-Rich Plasma — Impact Sports Medicine & Orthopedics (impactsportsnashville.com)
If you would like to discuss the concept of Proactive Interventional Orthopedics and how this may be a benefit to you in 2023, then please give us a call. We would love to customize a treatment protocol for you.
Why Insurance Does Not Pay For Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections
/Platelet-rich plasma injections, commonly known as PRP, have been utilized in orthopedics for at least the past 15 years. The first studies in orthopedics looked at PRP being utilized for tennis elbow, and the results were promising.
Fast forward 15 years and now platelet rich plasma has become a mainstay in the treatment of many orthopedic conditions, ranging from osteoarthritis to tendon and ligament problems. An estimated 60% of orthopedic practices now offer PRP to their patients and while some physicians can claim true expertise in this type of treatment, other practices remain novices when it comes to the application of PRP.
Now, to answer the question in the title of this blog, “why do insurance companies not cover PRP….” We will provide an educated opinion with several bullet points.
-Many insurance companies claim that PRP injections are “experimental.” Experimental is a very broad term that can be applied in numerous ways. What classifies something as experimental? In my opinion, this is something that has been utilized for a very short period of time and has very few studies or anecdotal pieces of evidence to demonstrate a sustained rate of efficacy. Meaning, this treatment hasn’t been used for very long, has not been used on very many patients, and we really don’t know what the short-term or long-term results are.
When it comes to PRP, I would say we are light years beyond the experimental stage. For many years, PRP has been used not only in orthopedics, but also in plastic surgery, wound care, dermatology/aesthetics and hair-loss situations, to just name a few. PRP has demonstrated a long track record of safety, and the overwhelming majority of studies demonstrate that patients benefit from these procedures. So, in my mind as a physician of nearly 25 years who has studied medical data for his entire career, I would no longer classify PRP broadly as experimental. Are more studies regarding PRP necessary? Of course. Yet this is true for every treatment in medicine. Trust me when I tell you that there are numerous treatments in all fields of medicine being utilized right now that have been studied far less than PRP.
-Next, the truth is that insurance providers these days are looking to pay for fewer and fewer of your medical expenses. We have to get away from the mentality that “I have health insurance, and it should cover all of my medical needs.” In truth, we are probably getting back to a model where insurance should be used for major health expenses and catastrophic situations, not for most of your routine day-to-day medical care. Almost all of private insurance companies are for-profit organizations. There’s nothing wrong with that. However, you must realize that their first goal is making a profit to sustain their business. Their first priority is not providing the optimal care for the patient, as often is the case, the optimal care is not the least expensive. So, we are constantly preaching to our patients these days that the best treatments in orthopedics are not necessarily the ones you can expect your insurance to cover.
-Finally, to partially take the side of the insurance company, an argument against covering PRP would be that it cannot be “standardized.” We can standardize a medication or certain forms of medical equipment, but we cannot standardize a patient’s blood. Therefore, one person’s PRP may not look like another patient’s PRP, meaning the number of platelets, white cells, etc. may be fairly variable between patients. Also, there are probably 20 to 30 commercially available PRP systems on the market now. None of these produce PRP in exactly the same way, once again, making the argument that PRP injections cannot be completely standardized. For this reason, insurance companies often take a pass on something they don’t view as uniformly the same treatment for every patient.
Now, let’s turn attention to why it really may not matter whether insurance companies cover PRP or not and why you should not be deterred from seeking this treatment.
-First, let’s look at the financial piece. So many of our private insurances require that we first meet our deductible before insurance will pay a significant portion of our medical bill. These deductibles are rising. Until you meet your deductible, you are going to pay out-of-pocket for any office visit, diagnostic test, medical procedure, or medication. Therefore, let’s say you were choosing between a steroid injection versus a platelet-rich plasma injection. Technically, the steroid injection is “covered by your insurance,” but until you meet that deductible, you are going to pay for an office visit and the cost of that steroid injection. So, “covered by insurance” doesn’t mean it’s an expense-free treatment.
-Next, that steroid injection may not be the best treatment for your particular condition. Let’s say you have a partial rotator cuff tear. You either don’t want or don’t need surgery for it. The steroid injection may temporarily alleviate symptoms, but certainly will not heal the partially torn tendon, and in fact, some patients worsen within weeks to months after a steroid injection. Thus, assuming you then are still seeking care for your shoulder pain and torn tendon, you will require additional tests and treatments. This may mean an MRI, a long course of physical therapy, additional medication, or even surgery. Those options, especially when combined, can be very expensive. Although platelet-rich plasma injections are not covered by insurance, they could be the long-term solution to your problem, saving you hundreds to thousands of dollars on other necessary potential treatments. Therefore, why not choose the treatment that will be most successful, not just the one that your insurance states that it covers?
-Finally, gone are the days that you can depend on insurance companies decide what is best for you and your health. I tell patients all the time that I literally could give them 10 steroid injections over the course of the year and cause bodily harm to them and their particular joint or tissue. Insurance companies would reimburse me to do this, often without question. Nevertheless, that is just not the right thing to do. I took an oath as a physician to “first do no harm” which I have continued to practice to the best of my ability. In addition, not only do I want to not do harm, but I also truly desire to help my patient. Therefore, I will help you choose what I believe to be the best and most customized treatment option for your particular situation. This is not always in line with what insurance companies would prefer that I do. I have no desire to be a “rogue” physician, but I’ve dedicated my career to developing an expertise to help my patients. Part of our ability to help our patients lies in the fact that we get to know them personally and their particular situations, goals, desires, comorbidities, and even their financial situations. Therefore, we work as a team with our patients to decide what we believe is best for them. Although it’s very natural to want to pay as little as possible but still get the best outcome, you just can no longer rely on insurance companies to have the authority over these decisions for you.
I realize what is said above gives you a lot to consider. I have a passion for educating our patients on the best treatments for their particular situation, and I am dedicating to doing that for the remainder of my career.
As always, please let us know if we can be of assistance to you!
F. Clarke Holmes, M.D.
Impact Sports Medicine and Orthopedics
It’s Time To Start Treating Your Arthritic Knee Like Your Car
/“Orthopedic Maintenance”…that’s a term you may start to hear, especially in our practice. For years, patients have been led to believe that in the case of their arthritis, there’s “nothing you can do about it” until you want or choose to have a replacement. Also, our medical system has been developed to be reactive instead of proactive, especially again in the setting of arthritis. So, let me ask you this, do you only take your car to the mechanic when you have a problem? If the answer is yes, then you are on the fast track to either a needing a new car or paying your mechanic a pretty penny for all the repairs your car will need! If you are a wise car owner, then you take your car in at regular intervals for the oil change, fluid additions, tire rotation, alignment, brake maintenance and various inspections. So I then ask, should you be doing the same for your arthritic knee? The answer is a resounding “Yes!”
So, what does orthopedic maintenance look like? In very general terms, it means that if your body has aches, pains or dysfunction, then it’s wise to jump on these earlier than later, avoiding the temptation to ignore symptoms, and think, “I’m just getting old.” This translates to seeing your orthopedic/sports medicine physician to confirm a diagnosis and discuss treatment and prevention strategies. Let’s focus on one of the most effective forms of non-operative treatment for knee osteoarthritis: injections
1) Steroid (cortisone) injections are great for acute pain, when it’s important to reduce symptoms and swelling quickly. Steroids are really a more “reactive” treatment, such as when a patient needs to feel better quickly for a major life event (a trip, visit with the grandkids, have to feel better for work, etc.) but can be proactive for a patient trying to stave off a knee replacement or is not a good candidate for knee replacement. For example, the elderly patient whose risk of knee replacement outweighs the benefit, planning two steroid injections a year for his/her symptomatic knee arthritis may allow the patient to feel less pain, move better, be at lower risk for a fall and have a greater quality of life.
2) Hyaluronic Acid/Viscosupplement injections (brand names include Orthovisc, Gelsyn, Euflexxa, etc.) have a long track record of excellent safety and provide symptomatic relief in approximately 75% of patients for 4-12 months. They probably work as anti-inflammatories and lubricants for the knee, replenishing the hyaluronic acid in the arthritic knee that is depleted or less effective. These are probably more beneficial for those with mild to moderate arthritis as opposed to more severe cases. There are essentially no side effects except for mild injection-site soreness in some. Most insurance companies will authorize this 3-4 injection series every 6 months, so planning on about two series a year is a very proactive strategy. These are what we often term as the “oil change” injections.
3) Orthobiologic injections are really your “game-changer” injections. These have been used in orthopedics for 15 years and in our practice for over 10 years. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) is the most commonly used orthobiologic injection. Insurance companies and even some medical providers still like to consider these as “experimental” or unproven treatments for osteoarthritis, yet there are now 39 randomized, controlled trials (studies) that demonstrate that PRP is effective in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis. PRP is derived from your own blood, as we obtain blood from an arm vein, spin this in a centrifuge, remove the majority of red and white blood cells, and concentrate the platelets which are rich in your own growth factors. These growth factors module inflammation, reduce pain, improve function, and most likely have a beneficial effect on the cartilage within the joint. This is how they are “game-changers.” They very likely stop or slow the progression of arthritis by stabilizing the cartilage and potentially improving the quality of the cartilage.
We typically start with two PRP injections 2-6 weeks apart and expect, on the average, 6-12 months of symptomatic benefit. Repeating these at regular intervals is likely the best plan of action in order to see continued, long-term benefits. PRP injections are here to stay, and how we continue to apply them in the treatment of osteoarthritis will continue to evolve.
Primary care providers and dentists have done a great job integrating maintenance evaluations and treatments into a patient’s health regimen. Now, we should likely be doing the same in orthopedics, and the treatment of knee osteoarthritis is a great place to start, as this is the most common medical condition seen in our office today. It is a tremendous source of pain and disability for millions of Americans and contributes to the spending of billions of health care dollars. It’s time for orthopedic physicians and patients to join together to be proactive over reactive and realize that less-invasive preventative strategies are preferred over more-invasive and costly interventions.
As always, we here to help and strive to be your resource for these innovative maintenance strategies!
F. Clarke Holmes, M.D.
Impact Sports Medicine and Orthopedics
What Supplements Might Be Useful In Orthopedics
/Many people prefer to try a natural approach when it comes to preventing conditions or treating symptoms by taking various vitamins and supplements. There are many options for supplements and vitamins out there, but are they really effective? Unfortunately, there is little education or research on these products.
Remember, the FDA does not regulate supplements and vitamins. Talk to your healthcare provider before beginning any supplements or vitamins. If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, discuss supplements and vitamins with your provider.
Here are a few common vitamins and supplements we discuss with our patients in orthopedics.
Turmeric
Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, turmeric is a great tool to help combat full body inflammation. We recommend a turmeric supplement that contains extract instead of ground root powder, 95% curcuminoids, curcumin, and bioperine (black pepper) to help with absorption. Daily dose recommendation is 500mg-2,000mg. Turmeric can slow blood clotting and should be avoided in those who take blood thinners, have bleeding disorders, anemia, gallbladder conditions, or pregnant. Caution should be used in those who take diabetes medication, as turmeric may make the effects of these medications stronger and therefore may result in hypoglycemia. Note: cooking occasionally with turmeric does not provide the amount needed to reach anti-inflammatory effects.
Glucosamine
Glucosamine is thought to increase cartilage and fluid around joints and/or help prevent cartilage breakdown, therefore, decreasing pain and improving function. Research studies’ results have shown conflicting information. Taking this does not reduce your risk of getting osteoarthritis. The recommended dose is 1,500mg daily. Do not take this supplement if you take warfarin (coumadin) as it increases the effects of warfarin, elevating your risk of serious bruising or bleeding. Do not take this supplement if you have personal or family history of glaucoma, are on cancer treatments, or have allergies to shellfish. Take caution if you have diabetes, as glucosamine has been shown to increase blood sugar levels and decrease the effectiveness of diabetic medications. Also, take caution if you are pregnant and/or breastfeeding, have asthma, glaucoma, hyperlipidemia (high cholesterol/triglycerides), and hypertension.
Chondroitin
Usually taken in combination with glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate is one of the building blocks of cartilage. Used to help decrease osteoarthritis pain and improve function. Recommended daily dose is 800-1,200mg. Do not take if you have prostate cancer or are pregnant/breastfeeding. Take caution in those with asthma. There is an increased risk of bleeding if taken with warfarin.
Hyaluronic Acid (HA)
HA’s action in orthopedics is to lubricate the joints and maintain normal joint cushioning to provide more support, resulting in decreased pain and increased functioning. In osteoarthritis and as we age, this substance becomes naturally depleted due to wear and tear. It comes in many different forms, but injections are the most widely used and most effective in sports medicine and orthopedics. We like to tell our patients to think of HA injections like an oil change for your knee; the oil is the HA substance and, your joints are the car. HA oral supplements have not shown to be effective for musculoskeletal use.
Vitamin D
Most people do not receive enough daily vitamin D from food and sun alone. Vitamin D has many benefits. From an orthopedic standpoint, vitamin D modulates inflammation, prevents involuntary muscle spasms, and cramps, and enhances calcium absorption into the bone which helps with bone growth and bone remodeling. Vitamin D plays a key role in helping prevent osteopenia and osteoporosis (thin and brittle bones). The recommended dose is 600-800 international units (IUs) daily, yet supplementing with 1000-2000 IUs of D3 is safe for most patients. Some patients are found to have vitamin D deficiencies with a blood test and will require higher dosing often for at least a month. Foods high in vitamin D include salmon, sardines, tuna, egg yolks, mushrooms, cow’s milk, soy milk, yogurt, orange juice, cheese, fortified cereal, and oatmeal.
Calcium
Calcium helps build and protect bones. A low calcium intake can result in fractures, osteopenia, and osteoporosis. Most people get enough calcium in their normal diet. The daily recommended amount of calcium needed is dependent on age.
1-3 years old: 700mg
4-8 years old: 1,000mg
9-18 years old: 1,300mg
19-50 years: 1,000mg,
51 years to 70 years: males 1,000mg and females 1,200mg
71 years and older: 1,200mg.
Who needs a calcium supplement? Those who are vegans, lactose intolerance, consume large amounts of protein or sodium, on long term steroid treatment, those who have inflammatory bowel disease and celiac disease, and those who do get enough calcium in the foods they eat. Overall, it is better to get the calcium your body needs through food instead of a supplement. There are some studies that have linked calcium supplements to heart disease, colon polyps, kidney stones, and heart attacks. Foods high in calcium: almonds, oranges, dried figs, soybeans, garbanzo beans, white beans, pinto beans, milk, yogurt, dark leafy green vegetables.
Ashwagandha
Ashwagandha helps in reducing anxiety and stress. On the label you want to look for root extract, as this is more potent that ground root powder. KSM-66 ashwagandha root extract has been studied in many clinical trials with positive outcomes. Daily dose recommended is between 500-1,500mg.
Potential side effects include gastrointestinal upset or headache. It can potentially lower blood pressure, lower blood sugar, and affect thyroid hormones, and in rare cases, have a negative effect on the liver. Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should not take this.
Taylor Moore, FNP-C
Impact Sports Medicine and Orthopedics
What is a Nurse Practitioner?
/I have had the pleasure to meet and take care of many of our awesome patients since I joined Impact Sports Medicine in August 2020. However, questions still occasionally arise about what my role is at Impact.
What is a Nurse Practitioner?
You may hear the following interchangeable terms: Nurse Practitioner, NP, Mid-level, Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN). Nurse Practitioners are trained to assess patient needs, order and interpret imaging and laboratory tests, diagnose conditions, formulate and prescribe treatment plans, and provide patient education. There are many different Nurse Practitioner Specialty degrees. You commonly see NPs in inpatient and outpatient settings, primary care, and specialist offices, occupational health, the health department, and more!
Are a Nurse Practitioner and a Nurse the same thing?
No, these are not the same roles and have different scopes of practice. A nurse assists providers and has an associates or bachelors degree, whereas an NP requires at least a masters degree and special training through an NP educational program.
Nurse Practitioners function as a provider just like a Medical Doctor (M.D.). In Tennessee, all Nurse Practitioners are required to be under the supervision of a Medical Doctor.
What is the difference between a Nurse Practitioner (NP) and a Physician Assistant (PA)?
These two roles function very similarly with tiny nuances. Both are considered mid-level roles. A Nurse Practitioner is required to be a Registered Nurse (RN) before advancing their training to become an NP.
What is my role at Impact Sports Medicine and Orthopedics?
I see patients independently of, and at times along side, Dr Holmes. This means I can assess and examine patients, interpret imaging and labs, prescribe medications, diagnose conditions, provide treatment plans, perform ultrasound guided injections, and provide education to patients. Overall, think of me as a provider extension of Dr. Holmes.
What else do I want you to know about me as an NP?
Although you will see me independently, Dr. Holmes and I work as a team. This means I discuss patient cases and my decisions with him, and always have him review x-ray and MRI images as well. I want patients to know he is involved in their care, even if you don’t see him directly. Yet, have confidence that I will deliver safe, compassionate, and competent care to get our patients better! I work with my patients as a team to devise decisions that are tailored to each individual, their conditions, and their needs.
Hopefully this provides more clarity on what a Nurse Practitioner is and my role at Impact Sports Medicine and Orthopedics. Looking forward to providing care to y’all in the future!
Taylor Moore, FNP-C
Instagram: @taylormoore_nashvillenp
Facebook: Taylor Moore, FNP-C
5 Reasons to Either Have or Avoid a Steroid/Cortisone Injection
/Steroid, often called “cortisone,” injections have been used in orthopedics and other specialties for several decades as potent anti-inflammatories. In recent years, they’ve become more controversial, as medical studies have validated that they likely have negative effects on our bodies and actually worsen certain conditions in the long-term. However, steroid injections still have some positive utility, and careful discussion with each patient must be undertaken to determine whether a steroid injection may be more beneficial or more harmful in each unique situation. Let’s explore those situations:
A Steroid Injection Can Be Particularly Beneficial in These Situations:
1) Adhesive Capsulitis- most commonly seen in middle-age women, this highly-inflammatory condition causing shoulder pain and stiffness often responds beautifully to an ultrasound-guided injection into the glenohumeral joint.
2) Early Phase of Tendonitis- if we catch tendonitis very early and when it’s primarily in the inflammatory stage (like tennis elbow or calcific rotator cuff tendonitis), a steroid injection can be very helpful in reducing pain and restoring function.
3) Diagnostic and Therapeutic- many times, we see a patient that has pain in an area, yet we can’t determine the exact source. Thus, we use a precisely-placed injection with ultrasound to see if the pain is relieved. If so, then we feel that we’ve located the source and can then customize a more effective treatment plan. We use this strategy often for hip pain.
4) A Patient Needs Rapid Relief- your knee is swollen and that bucket-list vacation that will require a lot of walking is fast-approaching. Your arthritic knee is in a flare, and we need to reduce pain and swelling within days, so that you can better enjoy that trip or upcoming event.
5) Gout and Pseudogout- these are highly-inflammatory conditions due to excessive urate or calcium deposits in a joint, respectively. A steroid injection can provide rapid relief from these conditions.
A Steroid Injection Should be Avoided in These Situations:
1) Chronic Tendonitis and Partial Tears- if you’ve had tennis or golfer’s elbow, rotator cuff issues or gluteal tendonitis for 3 months or greater, then your tendon likely has more degeneration and tearing than just inflammation. Steroid injections are far less likely to provide a long-term benefit in these situations.
2) Repetitively- unfortunately, many patients make it to our office after having had 3-5 steroid injections over the past 1-2 years for their chronic condition such as tennis elbow or plantar fasciitis. We know that steroid injections have a catabolic (causing further deterioration) effect on joints and soft tissues if used excessively.
3) Around Tendons at Risk for Rupture- the patellar tendon and Achilles tendon are two areas where we always avoid steroid injections. These tendons are prone to major tears, especially if exposed to injectable steroids.
4) Risk of Infection- if there is any suspicion for an infection in a joint or bursa, then steroid injections are a “no-go.” It’s better to aspirate the fluid and send for analysis first before considering a steroid.
5) Surgery in the Near Future- if a patient is considering having a joint replacement in the next 3 months, then steroid injections should be avoided due to the risk of infection during and shortly after the surgery.
We hope you find this information helpful when it comes to one of the most commonly proposed non-surgical treatment in orthopedics. As always, let us know if we can be of help to you!
-F. Clarke Holmes, M.D.
Impact Sports Medicine and Orthopedics
Will My Heel Pain Ever Go Away?
/In middle-age individuals, 90% of the time, heel pain is caused by plantar fasciitis. The plantar fascia is a soft-tissue band, technically a ligament, that supports the hindfoot and midfoot. It is quite prone to inflammation, degeneration and tearing. It is a stubborn problem to both endure and to treat, and commonly becomes a condition that last months to occasionally years. However, do not fear, we have solutions for you!
How Does it Present?
· Heel pain, often sharp, with the first few steps out of bed and after a long day on your feet
· Pain when rising from a seated position after prolonged sitting, such as in a car
· In endurance athletes, pain during and after exercise
· Tenderness on the bottom of the foot, specifically at the heel where the plantar fascia originates
Why Did I Get This?
· Age- middle-agers are prone to this, as they are very active, but their rate of tissue breakdown exceeds their body’s repair rate. This is why younger individuals do not typically get this problem. They have a faster healing rate.
· Poor footwear- shoes that are flimsy, too old or generally unsupportive contribute
· Weight- gaining weight or being overweight overloads the tissue at the lowest point of our body
· Too much activity/overuse- runners, walkers, and athletes repetitively load the plantar fascia, and at times, are in a situation of overuse or too much, too soon
· Poor biomechanics- tight or weak calf muscles, a high arch or flat foot or a foot that excessively pronates or supinates can all contribute
How Do I Treat It?
Patience is the key. Let’s repeat that….patience is the key. This condition often requires months of treatment. Recovery can be slow. The underlying risk factors listed above must be corrected. What works for one patient may not be the best treatment for another. Care must be individualized.
· Rest- yes, this is a dirty, four-letter word for many patients. Plantar fasciitis will NOT improve as long as one continues to run, walk or exercise to the same degree. Sometimes, activity modification will work- fewer miles, less frequent high-impact exercise and/or trying something lower impact such as biking or swimming
· Improve the footwear and minimize going barefoot- remember with shoes, you often get what you pay for. Don’t go cheap!
· Physical Therapy- helps most patients, can be curative for those with mild cases. Will not get the job done by itself for moderate to severe cases.
· Orthotics/Inserts- over-the-counter or custom. OTC ones are less expensive and worth a try for mild cases. Custom are more expensive but are more successful for most patients. Orthotics alone usually will not cure plantar fasciitis. Other treatments must be combined.
· Anti-inflammatory medications- helpful in mild cases caught early. Not helpful in more severe cases or in patients that have had the problem for months or longer.
· Cortisone injections- occasionally helpful, more often harmful. We rarely utilize these, as they don’t promote healing, only reduce inflammation and can increase the risk of further tearing of the fascia. NEVER get a series of 3 cortisone injections as recommended by some.
· Orthobiologic injections- very helpful for most. These are meant to “heal the heel!” Platelet-rich plasma injections introduce numerous growth factors to the area to improve the tissue environment and thus, are typically successful in promoting healing of the fascia while reducing pain and improving function. These are game-changing injections and ones we have provided under ultrasound-guidance successfully now for many years.
· Surgery- we favor a minimally-invasive procedure called the Tenex procedure. Tiny incision, local anesthesia only, no stitches required with minimal healthy tissue disruption. The “old-school” surgeries require larger incisions and involve “releasing”/cutting the fascia off the bone, are less successful, higher risk and have been abandoned by many orthopedic surgeons.
What to Avoid:
1) Stretching the bottom of the foot. An example is when you pull the toes back towards you. Most cases of PF involve inflammation and/or tearing of the fascia. Stretching damaged or inflamed tissue is often counterproductive
2) Pushing through the pain with exercise. If you have PF, you have to relatively rest, which may mean temporarily discontinuing running, walking, jumping, etc. or at least, reducing your distance or frequency of these activities.
3) Skimping on shoes and/or orthotics. The old adage, “you get what you pay for…” applies here. Think of purchasing high-quality athletic and everyday shoes as well as orthotics (inserts) as an investment in your health and quality of life. At times, the more expensive orthotics are worth the extra cost.
In conclusion, heel pain affects a high percentage of middle-age individuals and can range from a nuisance problem to a disabling one. The key here is to seek care early and from someone who can customize a well-constructed treatment plan for you that has a variety of quality interventions. We are here to help!
Five Mistakes to Avoid with Plantar Fasciitis
/Plantar Fasciitis is the most common cause of heel pain, most commonly seen in middle-age individuals. There are numerous treatment options, yet with our decades of experience in treating this problem, we’ve found many pitfalls, and thus, here’s a list of what NOT TO DO!
1) Stretching the bottom of the foot. An example is when you pull the toes back towards you. Most cases of PF involve inflammation and/or tearing of the fascia. Stretching damaged or inflamed tissue is often counterproductive
2) Pushing through the pain with exercise. If you have PF, you have to relatively rest, which may mean temporarily discontinuing running, walking, jumping, etc. or at least, reducing your distance or frequency of these activities.
3) Skimping on shoes and/or orthotics. The old adage, “you get what you pay for…” applies here. Think of purchasing high-quality athletic and everyday shoes as well as orthotics (inserts) as an investment in your health and quality of life. At times, the more expensive orthotics are worth the extra cost.
4) Having multiple cortisone/steroid injections. It’s probably best to avoid steroid injections altogether for PF, yet a one-time steroid injection can occasionally be indicated for the patient that is miserable due to severe heel pain. Repetitive steroid injections often result in long-term worsening of this condition.
5) Not being patient. PF resolves in 95% of individuals with the proper customized treatment, yet it often is a 6 to 12-month process. Don’t give up on certain treatments too soon, as most interventions work gradually over weeks to months, including footwear changes, night splints, relative rest, physical therapy, orthotics and orthobiologic/regenerative injections.
If you are struggling with plantar fasciitis, then we are here to help!
Clarke Holmes, M.D.
My Elbow Really Hurts, and I Feel Like a Wimp!
/We hear this comment or one very similar to it on a frequent basis. Good ole’ tennis elbow, also know as lateral epicondylitis. Despite these names, this is not a problem limited to tennis players and does not typically involve the bone on the outside of the elbow named the lateral epicondyle. It is actually a tendon problem. The common extensor tendon on the outside of the elbow is highly involved in gripping, grabbing and lifting. When you shake someone’s hand, this tendon is under a lot of stress. When you lift the coffee mug with a handle, the positioning of your wrist transmits stress to this tendon. When you pull your sheets up to you when in bed, the position and action of the wrist and forearm send stress to this tendon. Finally, when this tendon is inflamed and/or partially torn, it HURTS! I mean, it really hurts. You are not a wimp for complaining about tennis elbow. Fortunately, this is one of my favorite conditions to treat. Why? For many reasons: we usually can cure this problem. Patients are so grateful to see this pain go away. Finally, it’s gratifying to see patients return to things they love to do after successful treatment such as tennis, golf, weight lifting, gardening and even typing!
Turning our attention to treatment options, there are traditional and innovative options. At Impact Sports Medicine and Orthopedics, we specialize in both types:
Traditional:
1) REST and changing the biomechanics- how and how much you lift, grip and grab
2) A wrist splint- yes, immobilizing the wrist and forearm unload the tendon far more than immobilizing the elbow
3) A cortisone injection- in our hands, 90% of patients experience relief with an ultrasound-guided injection. However, since tendon damage is often the cause of the stubborn pain, cortisone, at times, may only provide temporary benefit.
4) Physical Therapy- helpful in changing the biomechanical problems that led to the tendon damage. However, the benefit can be limited if tendon is partially torn.
Innovative:
1) The Tenex procedure- a true game-changing minimally-invasive procedure. This is our favorite option for those patients that have not improved with the traditional treatments. Local anesthesia only, a tiny incision, 2 minutes of tendon treatment with a small probe, no stitches, typically covered by insurance and a 90% success rate. How does that sound? We've loved this procedure for 7+ years.
2) Orthobiologic Injections- platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections are very solid choices, isolating and concentrating the platelets from you own blood. This becomes a solution rich in human growth factors utilized to stimulate healing of the tendon.
3) Nitroglycerin patches- placed on the skin over the tendon, these are good choices for those patients needing something extra, but prefer a treatment that is non-invasive. These work by producing nitric oxide in the tissues, which then can be responsible for tendon healing.
In summary, we hate that you have "tennis elbow," but always appreciate the opportunity to treat you. It's our mission to make this common cause of elbow pain leave your life and never return! Let us know if we can help.
-F. Clarke Holmes, M.D.
Will Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Injections Replace Cortisone?
/The answer to this question is simple: Yes, No and Maybe. Platelet-Rich Plasma injections have taken the orthopedic world by storm. Why is this? They are safe. They are natural. They can be done in the office in a short period of time. They may prevent surgery in some cases. They can be disease-altering, not just symptom-reducing. Most importantly, in many cases of tendon, ligament and joint problems, they are EFFECTIVE.
PRP injections involve drawing blood from a patient’s vein, typically in the arm. Then, the blood is centrifuged (spun) to separate out the red and white blood cells, while simultaneously concentrating your own platelets. Our platelets are known to have numerous growth factors that serve many beneficial roles in our musculoskeletal tissues. This concentrated solution is then injected under ultrasound-guidance back into an area of damage, such as a partially torn tendon, the plantar fascia or an arthritic joint. We believe that these platelets help to modulate unhealthy inflammation that resides in damaged tissues. This helps over the long-term to reduce pain and subsequently, improve function. In some cases, damaged soft tissue can heal in the presence of these concentrated platelets. In other cases, the deterioration often seen in cases of osteoarthritis can be slowed or halted. Thus, there are some preventative benefits of PRP.
Cortisone injections, known medically as steroids, have been around for decades. They simply are very strong anti-inflammatories. They can reduce pain and swelling within hours to days of an injection. However, they are known to have catabolic, or “breakdown” effects, meaning, numerous exposures to steroids can worsen the structure and strength of a soft tissue or joint. They also can produce short-term systemic side effects, including fluid retention, headache, insomnia, changes in emotions, skin flushing/redness and increases in blood sugar, particularly in diabetics. Cortisone injections are still used quite frequently to treat tendonitis, arthritis and disc problems in the spine.
Now, back to the question in the title. In our practice, we still use both types of injections. However, the percentage of PRP injections is increasing, while the percentage of cortisone is dropping. Why? We want our patients to have “game-changing” treatments whenever possible. We want conditions to improve over the long-term. We want to stop that deterioration process and to promote healing when possible. Also, we know that in the case of cortisone injections, some patients feel so good, so quickly, that they are prone to re-injure themselves. Thus, short-term improvement, but long-term worsening with some cortisone injections.
Thus, how do we choose what type of injection to recommend to a patient? Here are some examples:
-A 60-year-old woman will be traveling on a bucket-list trip to Italy in one week. Her arthritic knee is painful and swollen, and she needs some quick relief to really enjoy this trip. We choose a CORTISONE injection to provide that relief. She will likely feel better within a few days of the injection and will probably see a benefit for 1-3 months.
-A 35-year-old runner tore his ACL at age 20 and had successful surgery. Now, he has mild osteoarthritis of the knee that is stiff in the morning, aches after long runs and occasionally swells. He is a great candidate for PRP. PRP should help his keep inflammation down, reduce his aches and preserve his cartilage in his knee for years to come.
-A 65-year old woman has had 2 weeks of lateral hip pain after a trip to the beach with frequent walking. She can’t sleep on the side of her painful hip and going up stairs is difficult. We diagnose her with trochanteric bursitis and gluteal tendonitis. A CORTISONE injection here may do the trick. She has an acute inflammatory response and needs some relief to simply sleep better at night and handle her activities of daily living with less pain.
-A 24-year-old recreational basketball player has patellar tendonopathy and pain every time he jumps and lands. Symptoms have been present for 6 months and despite physical therapy, a brace and NSAIDS, he is only 50% better. We offer him 1-2 PRP injections. We need to promote healing of that tendon. We want long-term reduction in symptoms and tissue improvement, so that he can continue to play basketball and with reduced risk of tearing the tendon. Plus, we never inject cortisone in or around certain tendons, including the patellar and Achilles tendons, due to the risk of tendon rupture.
-A 70-year-old has mild to moderate hip and knee osteoarthritis. He can play golf a couple days a week, but relies on frequent doses of ibuprofen after his golf games and on days he plays with his grandchildren. His hoping to avoid joint replacement in his lifetime and knows that long-term use of NSAIDs is not good for his blood pressure, stomach or kidneys. We offer him PRP as a great option, with an injection into the knee and hip joints on the same day. He then will return a month later for his 2nd set of injections. After that, we hope and expect that he will have less pain and better function for 6 to 24 months, while also lowering his chances of joint replacement in the intermediate future. These PRP injections can be safely repeated months to years later, if necessary.
These are everyday examples of how we customize our treatments for patients based on their symptoms, diagnosis and goals. Age of the patient can play a role, but one is never “too old” to have a PRP injection. When head-to-head studies compare PRP to steroid injections, PRP is declared the “winner” the large majority of the time. Thus, we know that for long-term benefits of many joint and tendon problems, PRP is the better choice.
In conclusion, cortisone/steroid injections are not going away any time soon. They still play a role in helping patients in select situations. However, the world of orthobiologic injections such as PRP will only continue to expand as we strive to find more natural and less-invasive ways to treat a variety of orthopedic conditions.
The 5 Biggest Mistakes Inexperienced Runners Make Leading to Injury
/1) Training for a ½ or full marathon when you’ve never run a 5K or 10K- because of variability of muscle types, bone density, running mechanics and the efficiency of oxygen consumption, not everybody was made to run long-distance races. Some great athletes are hardly capable of running 5 miles. Then, you have those individuals who can run a ½ marathon and barely train to do it. If a novice runner, see what your body is capable of first by training for and completing shorter races before attempting much longer runs.
2) Pushing through pain to get through a run- there’s fatigue, soreness, the muscle burn and then, there’s pain. Concerning pain includes sharp discomfort, pain that results in limping, constant pain and pain associated with swelling. Pain around a tendon or right over a bone is a warning sign. Don’t ignore the “check engine light” that comes on in your body. Learn to recognize the difference between the types of discomfort and seek medical attention when the concerning form of pain is present.
3) The wrong footwear- this can be shoes that are too old or the wrong type for your foot and particular gait pattern. It’s time for new shoes when there’s visible wear of the tread, especially in the forefoot area (the third of the foot closest to the toes). Shoes should be updated every 300-500 miles or every 9-12 months, whichever comes first. Also, seek a true “fitting” for your shoes. The right size, width and style (stability, neutral, zero drop, etc.) are important choices, and you should avoid choosing the latest “fad” shoe or the one that has the coolest design simply for the fashion statement. Find a quality running store that can help you with these choices.
4) Training with a partner of a different skill set- it’s generally best to train with someone of a similar skill set and set of goals. Many runners are competitive (whether they admit it or not!), and will push each other at times even on training runs. While this is not all bad, someone training for their first ½ marathon will likely struggle to keep up with someone that has run numerous long-distance races. What’s the net result? The inexperienced runner tries to keep up with the experienced runner in terms of speed, distance and mindset. This is a recipe for injury. If wanting to train with a partner, try to find one that is willing to follow a similar schedule and runs a similar pace.
5) Making up for lost time- sometimes a training schedule gets derailed. An illness, an injury or a life event knocks a runner off his/her training schedule for a couple of weeks. Race day is nearing, and thus, the runner tries to advance the training schedule by increasing the number of running days each week or jumping ahead and doing more miles or longer runs than what he/she should be doing. Example: it’s late in the training schedule for a ½ marathon, and the longest run you’ve done is 7 miles. You missed 2 weeks of training because of a sinus infection. You jump ahead on the schedule and do 10 miles on a Saturday. Now, your shin is throbbing. Shin splint or stress fracture? Either way, you’re done! No race for you. No running for weeks to months. What should you have done instead? Resumed your training schedule where you left off before the illness. Then, if not ready for this race, postpone and run another one. There are ½ marathons within a region almost every weekend, especially from the late winter until the late spring. Or, you could have still run the race, but adjusted your goals. Maybe you change your mindset to just finishing the race, even it meant walking part of race. The bottom line: skipping steps in your training often results in an increased risk of injury.
At Impact Sports Medicine, we would rather help you prevent an injury, but when one does occur, we are ready to help! Enjoy your running!